Table of Contents
Gum disease is one of the most common oral health issues affecting millions of people worldwide. It can lead to severe dental problems if left untreated, including tooth loss, which can significantly impact your quality of life. At Montana Center for Implants and Dentures, we understand the critical role that healthy gums play in maintaining overall oral health and the importance of addressing issues promptly. In this article, we’ll explore the causes, progression, and how dental implants can offer a solution for those who have experienced tooth loss due to gum disease.
What is Gum Disease?
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is an infection of the tissues that surround and support your teeth. It typically starts with bacterial growth in your mouth and, if not properly managed, can lead to the destruction of the gum tissue and the bone that supports your teeth. It is a progressive condition, meaning it worsens over time if left untreated.
There are two primary stages:
- Gingivitis: This is the early stage. It is characterized by red, swollen gums that may bleed easily when brushing or flossing. Gingivitis is often painless, and as a result, many people may not even realize they have it. The good news is that gingivitis is reversible with good oral hygiene and professional dental care.
- Periodontitis: If gingivitis is not treated, it can advance to periodontitis. In this more severe stage, the gums begin to pull away from the teeth, forming pockets that become infected. The body’s immune system responds to the infection, but the combination of bacterial toxins and the body’s natural response can break down the bone and connective tissue that hold teeth in place. Over time, this can lead to tooth loss.
Causes of Gum Disease
Understanding the causes is essential for prevention and early intervention. Several factors contribute to the development of gum disease:
1. Poor Oral Hygiene
The most significant cause is inadequate oral hygiene. Failing to brush and floss regularly allows plaque—a sticky film of bacteria—to build up on the teeth. Over time, this plaque hardens into tartar, which can only be removed by a dental professional. The bacteria in plaque and tartar irritate the gums, leading to inflammation and the development of gum disease.
2. Smoking and Tobacco Use
Smoking and the use of other tobacco products are major risk factors. Tobacco weakens the immune system, making it more difficult for the body to fight off gum infections. Additionally, smoking impairs the healing process, making it harder to reverse gum disease once it has developed.
3. Genetics
Some people are more susceptible to gum disease due to their genetic makeup. If you have a family history of gum disease, you may be at a higher risk and should take extra precautions to maintain your oral health.
4. Hormonal Changes
Hormonal fluctuations, such as those that occur during pregnancy, puberty, menstruation, and menopause, can make gums more sensitive and susceptible to gum disease. Pregnant women, in particular, should be vigilant about their oral hygiene, as gum disease during pregnancy has been linked to adverse pregnancy outcomes, such as preterm birth.
5. Medications
Certain medications can affect oral health and increase the risk. For example, medications that reduce saliva flow (dry mouth) can lead to a buildup of plaque, as saliva plays a crucial role in washing away food particles and neutralizing acids produced by bacteria.
6. Chronic Illnesses
Diseases such as diabetes, heart disease, and rheumatoid arthritis are linked to an increased risk of gum disease. Diabetic individuals, in particular, are more prone to infections, and may have a more challenging time controlling the condition.
7. Poor Nutrition
A diet lacking in essential nutrients, particularly vitamin C, can compromise the immune system and make it more difficult for the body to fight off infections, including those that affect the gums.
8. Stress
Chronic stress can weaken the immune system, making it harder for the body to ward off infections. Additionally, stress may lead to neglecting oral hygiene routines, further contributing to the development of gum disease.
The Connection Between Gum Disease and Tooth Loss
Progressing from gingivitis to periodontitis can lead to gum and bone damage, potentially resulting in tooth loss. In fact, gum disease is the leading cause of tooth loss in adults. When the bone that holds the teeth in place is destroyed, teeth become loose and may eventually need to be removed or may fall out on their own.
Tooth loss not only affects your ability to eat and speak properly but also has a significant impact on your appearance and self-esteem. Missing teeth can cause the facial structure to collapse, leading to a sunken appearance and making a person look older than they are. Fortunately, advances in dental technology, such as dental implants, offer a solution for those who have lost teeth.
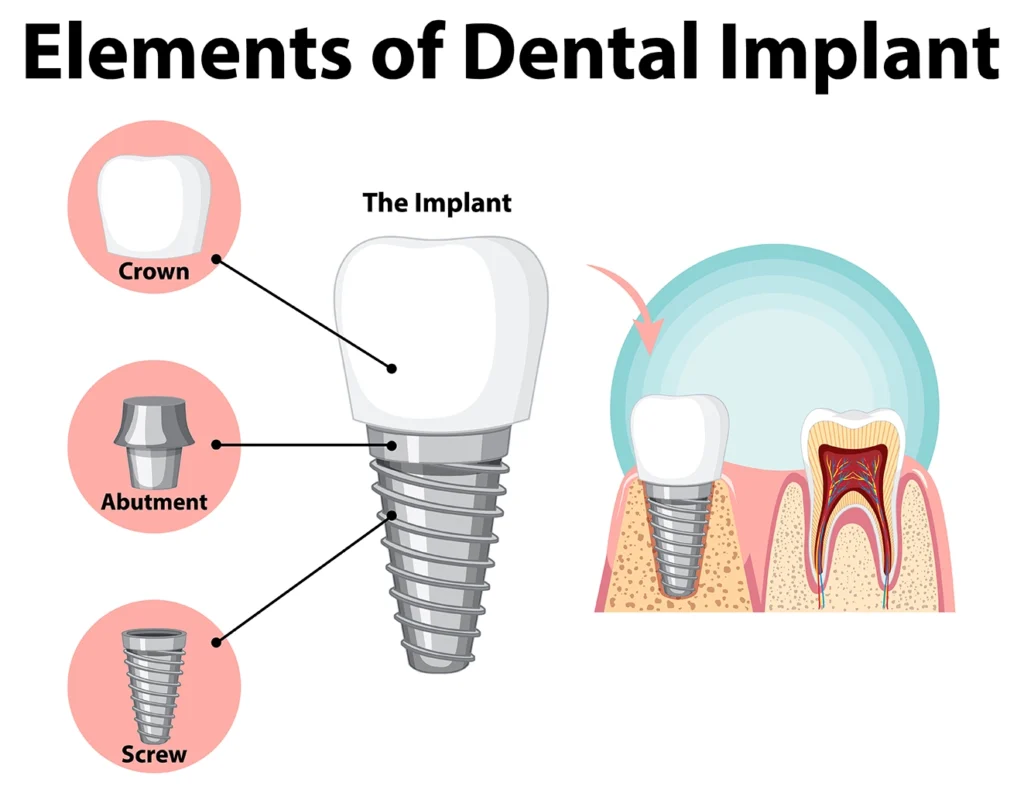
How Dental Implants Can Help
Dental implants are a revolutionary solution for replacing missing teeth. They offer several advantages over traditional dentures and bridges, making them an ideal choice for those who have lost teeth due to gum disease.
What Are Dental Implants?
Dental implants are artificial tooth roots made of biocompatible materials, such as titanium, that are surgically placed into the jawbone. Once in place, the implant fuses with the bone in a process called osseointegration, creating a stable and durable foundation for a replacement tooth or dental crown.
The visible part of the implant, known as the crown, is custom-made to match the color, shape, and size of your natural teeth, providing a seamless and natural-looking smile.
Benefits of Dental Implants
- Preservation of Bone Structure: One of the most significant benefits of dental implants is their ability to prevent bone loss. When a tooth is lost, the underlying bone begins to deteriorate due to the lack of stimulation that the tooth root provides. Dental implants stimulate the jawbone just like natural tooth roots, helping to preserve the bone and maintain facial structure.
- Improved Functionality: Unlike dentures, which can slip or cause discomfort, dental implants are securely anchored in the jawbone, providing stability and functionality similar to natural teeth. This allows you to eat, speak, and smile with confidence.
- Longevity: With proper care, dental implants can last a lifetime, making them a cost-effective solution for tooth replacement.
- Aesthetic Appeal: Dental implants are designed to look and feel like your natural teeth, restoring your smile and boosting your self-esteem.
Can People with Gum Disease Get Implants?
If you have lost teeth due to gum disease, you may be wondering if you are a candidate for dental implants. The good news is that many people with a history of the disease can still benefit from implants. However, it’s essential to address any active gum disease before undergoing implant surgery.
At Montana Center for Implants and Dentures, Dr. Josh Muir and Dr. Tanner Townsend will conduct a thorough examination to determine if you are a suitable candidate for implants. If it is present, we will develop a personalized treatment plan to manage the condition and prepare your gums and jawbone for implant placement.
In cases where significant bone loss has occurred, bone grafting procedures may be necessary to build up the bone and create a stable foundation for the implant. Our team is skilled in advanced implantology techniques and will guide you through every step of the process to ensure the best possible outcome.

Preventing Gum Disease and Protecting Your Implants
Whether you are trying to prevent gum disease or have already received dental implants, maintaining excellent oral hygiene is crucial. Here are some tips to keep your gums healthy and protect your implants:
- Brush Twice a Day: Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste to brush your teeth and gums at least twice a day. Pay special attention to the gum line, where plaque tends to accumulate.
- Floss Daily: Flossing is essential for removing plaque and food particles from between your teeth and around your implants. Consider using a floss threader or interdental brushes for easier access.
- Use an Antimicrobial Mouthwash: Rinsing with an antimicrobial mouthwash can help reduce bacteria in your mouth and prevent gum disease.
- Visit Your Dentist Regularly: Regular dental checkups and cleanings are vital for monitoring your gum health and ensuring the longevity of your implants. At Montana Center for Implants and Dentures, we recommend visiting our office every six months for a comprehensive examination and professional cleaning.
- Quit Smoking: If you smoke, quitting is one of the best things you can do for your gum health and the success of your implants. Smoking impairs healing and increases the risk of implant failure.
- Maintain a Healthy Diet: Eating a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals supports your immune system and helps keep your gums healthy.
Conclusion
Gum disease is a serious condition that can lead to tooth loss and other significant health problems if not addressed promptly. However, with the right care and intervention, it is possible to manage gum disease and restore your smile with dental implants. At Montana Center for Implants and Dentures, we are committed to helping you achieve optimal oral health and providing you with the best possible care. Whether you need treatment for gum disease or are considering implants, our team of experts is here to support you every step of the way. Contact us today to schedule a consultation and take the first step toward a healthier, more confident smile.




